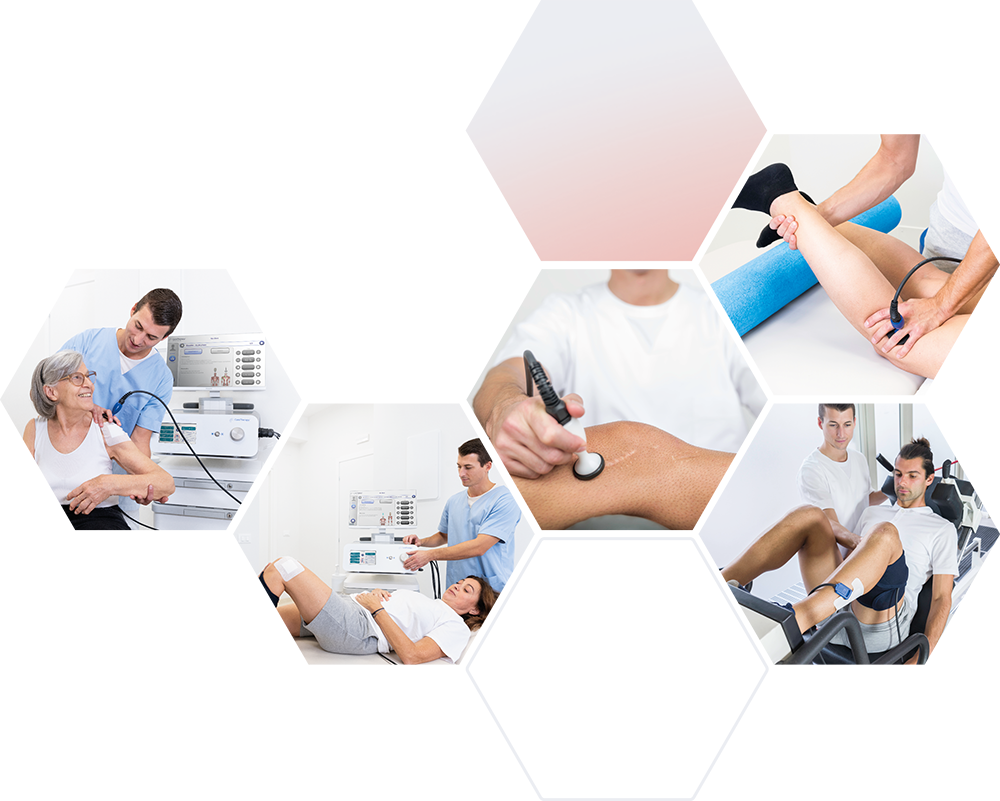
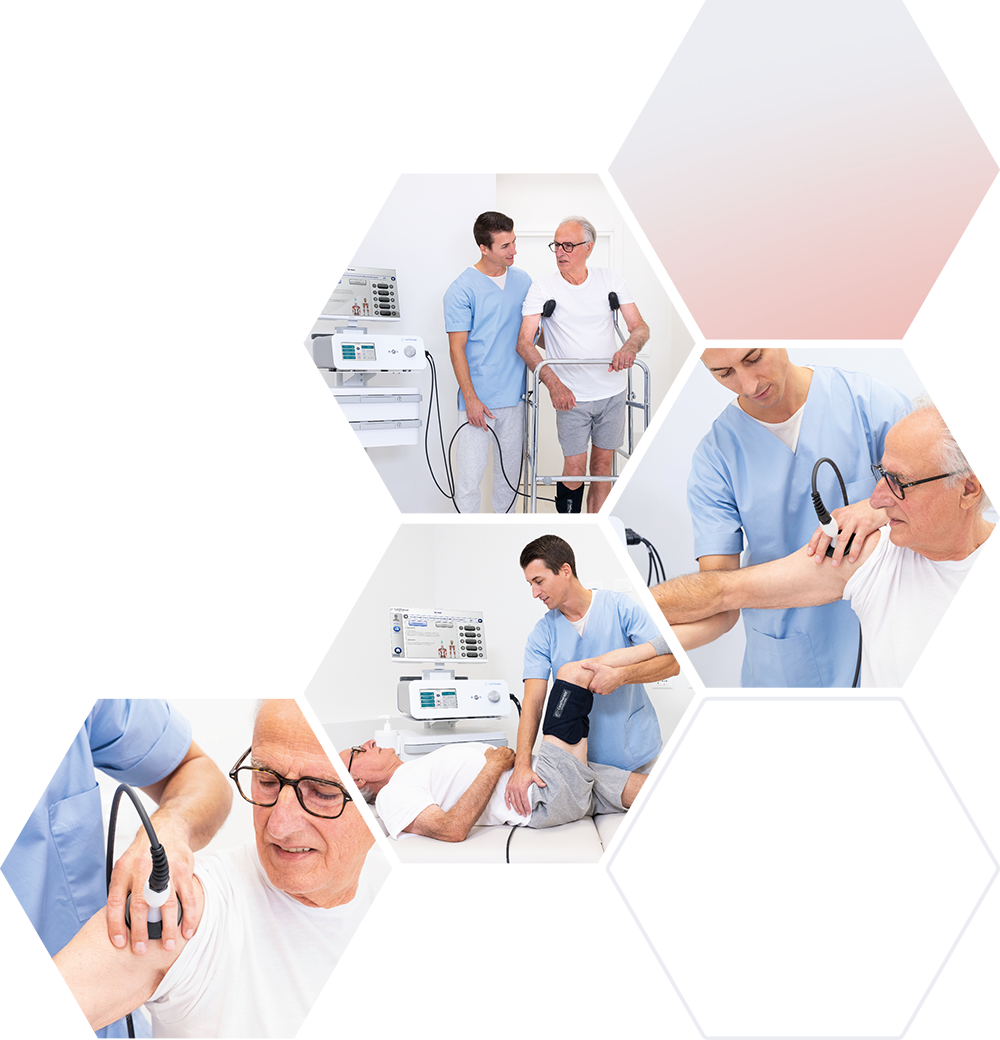
Vasodilation of the arterial, venous and lymphatic sectors necessarily causes an increase in blood-lymphatic flow with a great improvement in drainage and therefore with a notable anti-edema action particularly useful in all situations of inflammation.
With the edema, the various algogenic kinins located within the inflammatory focus (bradykinins, catecholamines, histamine, PGE2, leukotrienes, etc.) are also removed, which, together with the neoformation of endogenous opioids, explain the marked analgesic action of the method.